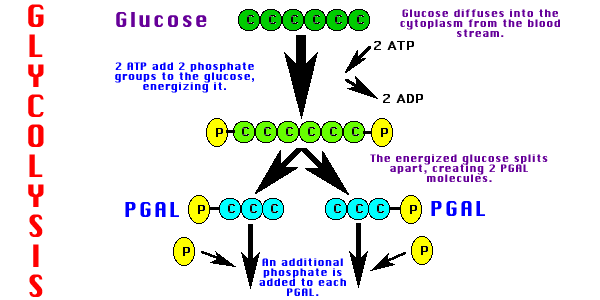
Glycolysis basically:
a) splits Glucose (6 C) to make two 3-carbon molecules. 2 ATP needed to split glucose.
b) removes energy and hydrogen from the 3-carbon molecules. This is used to make NADH (E. carrier).
c) removes more energy to make 4 ATP. 2 ATP go to split next glucose. 2 ATP available for cell use.
d) At end of glycolysis, 2 pyruvate molecules (3C) left.

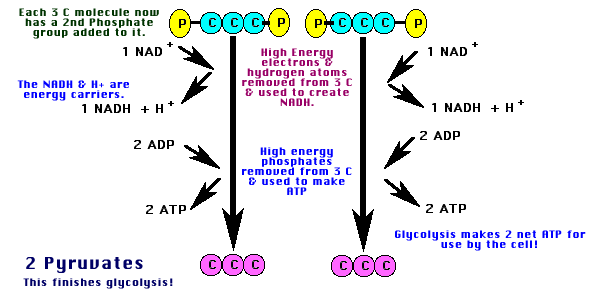
|
Summary of Glycolysis
|
| 1. One glucose (6C) converted into 2 pyruvates (3C). |
| 2. Net yield of 2 ATP for use by cell. |
| 3. Two NAD+ are converted into 2 NADH & 2H+. (These go to Electron Transport.) |
[Anaerobic Respiration (Fermentation)] [Aerobic Respiration]
Slichter