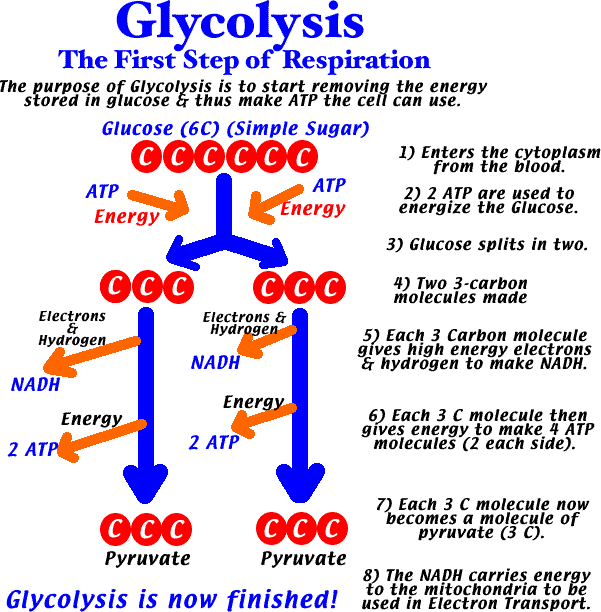
Glycolysis is the first step of reactions that break glucose apart to liberate the energy it holds in its C-H bonds.
Glycolysis occurs in the cell cytoplasm.
As a set of reactions, Glycolysis does not need the presence of oxygen.
Glycolysis occurs in both aerobic (with oxygen) and anerobic (does not need oxygen) respiration!

|
Summary of Glycolysis
|
| 1. One glucose (6C) converted into 2 pyruvates (3C). |
| 2. Net yield of 2 ATP for use by cell. |
| 3. 2 NADH are made. (These carry energy & Hydrogen to Electron Transport.) |