EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE
[Diagram of Typical Animal
Cell] ---- [Diagram of
Typical Plant Cell]
Intracellular Organelles
Cells
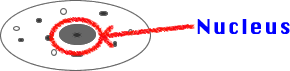
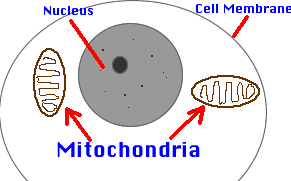
1) Nucleus: Control center of
cell.
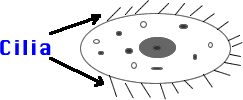
2) Cilia: Short hairs on cell membrane used for movement.
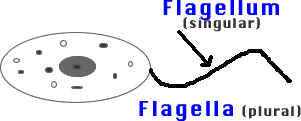
3) Flagella: Long hairs on cell membrane used for movement.
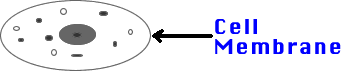
4) Cell Membrane: Thin covering of all cells. Controls what
enters or leaves the cell. Protects the cell from injury.
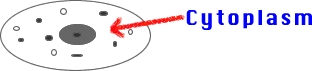
5) Cytoplasm (Protoplasm): The jelly-like liquid insides of
a cell. Found between all cell organelles.
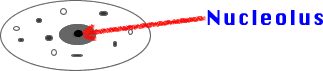
6) Nucleolus: Area of nucleus (looks like a dark dot) that makes
ribosomes.
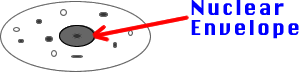
7) Nuclear Envelope: Thin membrane covering around nucleus.
Controls entry into & out of nucleus.
8) Mitochondria: Powerhouse of cell.
Chemically "burns" sugar to make energy for cell to use.
9) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): Tubes for transport and manufacture
of large molecules. Organizes cell interior.
a) Smooth ER : Lack ribosomes
so smooth surfaced tubes.
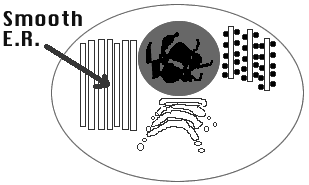
b) Rough ER : Tubes covered
with dot-like ribosomes.

10) Ribosomes: Place where cell proteins are made. Look like
dots on rough ER.
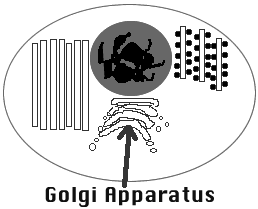
11) Golgi Apparatus (Bodies): Place
where molecules are finished and packaged into vacuoles.
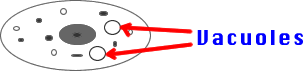
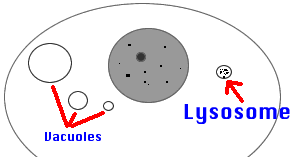
12) Vacuoles: Bubbles or "bags" for storage of food,
water, chemicals, or wastes.
 ------------
------------
13) Lysosomes: Vacuoles that hold digestive enzymes. Help get
rid of wastes or to digest cell food.
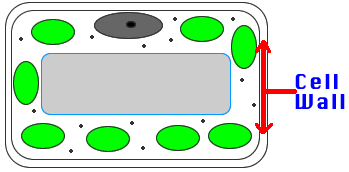
14) Cell Wall: Tough outer covering of all plant cells. Made
of cellulose. Not found in animal cells.
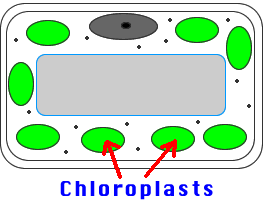
15) Chloroplasts: Site of photosynthesis
(Changes light energy into sugar energy). Found in most plant cells.
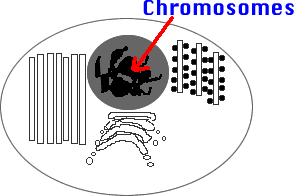
16) Chromosomes: Threadlike segments of DNA in nucleus. Contains
all genetic info for building the cell and controlling its daily activities.
Slichter












 ------------
------------




