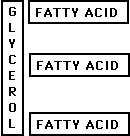
 A.
Triglycerides (fats) = glycerol + three fatty acids
A.
Triglycerides (fats) = glycerol + three fatty acids
1. Energy storage- Fats & oils store energy for long time periods.
2. Chemical messengers- Steroid hormones (testosterone & estrogen, etc)
3. Lipid bilayers of cell membranes (phospholipids)
 A.
Triglycerides (fats) = glycerol + three fatty acids
A.
Triglycerides (fats) = glycerol + three fatty acids
They are nonpolar (don't dissolve well in water). Only the ends of the fatty acids can be attracted to water.
They tend to form circular blobs in water with the nonpolar glycerol inside, the fatty parts facing to water.
[How Triglycerides are Formed]
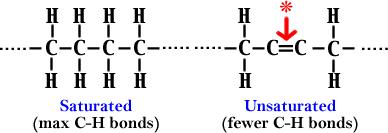
Saturated: all single bonds (many C-H bonds), hard, animal fats
Unsaturated: some double bonds (less C-H bonds), liquid, plant oils
 ......-----
......-----
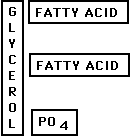 B.
Phospholipids: comprise cell membranes & soaps (Made of glycerol +
2 fatty acids + 1 phosphate )
B.
Phospholipids: comprise cell membranes & soaps (Made of glycerol +
2 fatty acids + 1 phosphate )
Polar PO4 faces outward
Nonpolar fatty acids face inward
[Polar nature of phospholipids]
a) lipid hormones
b) cholesterol
c) vitamins (Vit. D)
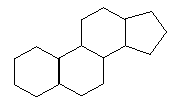
D. Waxes
 ----------------
----------------
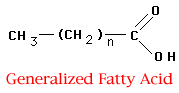
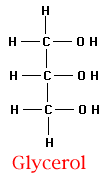
Be aware that Glycerol may also be drawn as follows (it's just rotated 90 ¾)
[Proteins] [Carbohydrates] [Nucleic Acids]