Exam Review Game for Cells & Microscopes
Print the following questions for your own review use.
Print the answer sheet for these questions.
Disclaimer: This game is for your use to aid in your review for the upcoming exam. Please be aware that because of the number of potential test questions, some questions have not been included in this game, so please review your notes and do other online reviews!
- List 2 advantages of using a light microscope instead of an electron microscope.
- List 2 advantages electron microscopes have over light microscopes.
- What term means a bubble-like structure used to store wastes, food, or chemicals within cells?
 What name is given to the stringy organelles that contain DNA in the cell nucleus?
What name is given to the stringy organelles that contain DNA in the cell nucleus?- What term means a special vacuole that contains digestive juices that a cell needs to digest its food?
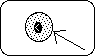
 What is the outer edge of a cell called? (This is an animal cell.)
What is the outer edge of a cell called? (This is an animal cell.)- Which cell organelle is called the powerhouse of the cell?
 What part of the cell is this? (the whole circular area)
What part of the cell is this? (the whole circular area)-
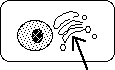
 What part of the cell is this dark dot?
What part of the cell is this dark dot?
 What part of the cell is this?
What part of the cell is this?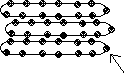 What term is given to the tiny round dots found in rough ER that are used to make proteins?
What term is given to the tiny round dots found in rough ER that are used to make proteins? What are these cellular tubes called?
What are these cellular tubes called?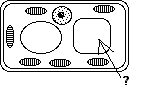 What are these 2 clear circular storage areas of a cell called?
What are these 2 clear circular storage areas of a cell called?- The outer surface of plasma membranes contains ID marker proteins. The molecule that makes the ID is not a protein but instead is a A) lipid, B) carbohydrate, C) fatty acid, D) amino acid.
- What is the name of the outer most boundary of a plant cell?
 What is the outer surface of this cell structure known as?
What is the outer surface of this cell structure known as?- What term means the jelly-like insides of a cell that surrounds all the organelles?
- What term means the outer-most boundary on an animal cell? It regulates what enters & leaves a cell.
- Name the green organelles found in plant cells where photosynthesis takes place.
- What term means the dark staining organelle found in the nucleus that is responsible for making ribosomes?
- What is the name of the chemical (nucleic acid) that makes up the bulk of a chromosome?
 What is the name of these long hair-like cell organelles?
What is the name of these long hair-like cell organelles?- Explain 2 differences between passive and active transport.
- Why is the Na-K pump an example of active transport, and how many Na+ leave and how many K+ enter the cell?
- List 2 types of organisms that are prokaryotic cells.
- List 2 ways that active transport is different from passive transport.
- What is the function of the nucleolus?
- What is the function of vacuoles within the cell?
- What does the mitochondria do within the cell?
- What does a cell use a flagella for?
- What kind of a carbohydrate is the cell wall of a plant cell made of?
- What kind of organic molecules are made by the ribosomes?
- What is the smallest thing scientists consider to be alive? (ie, What is the building block of all all living things?)
- What job do the lysosomes fulfill for the cell?
- Define diffusion.
- Do molecules tend to move from high to low concentration, or from low to high concentrations?
- Look at the diagram.
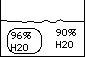 Will water flow into, out of the cell, or are they at equilibrium?
Will water flow into, out of the cell, or are they at equilibrium?
- Look at the diagram.
 Will water flow into, out of, or are they in equilibrium in the cell?
Will water flow into, out of, or are they in equilibrium in the cell?
- Explain in terms of osmosis why a slug dies when it is put into a beaker of salt water.
- What is meant by the term active transport?
- Describe what is meant by the term facilitated diffusion.
- What happens during exocytosis?
- State the 3 parts of the Cell Theory.
- Modern complex cells with internal organelles are classified as A) Eukaryotic cells or B) Prokaryotic cells.
- Cell specialization means that many cells are uniquely suited to perform a particular function within the whole organism. True or False
- What is the purpose of cholesterol in plasma membranes?
- What happens to a cell during endocytosis?
- What happens during phagocytosis?
- Define what a semipermeable membrane is.
- Why do cells remain small in size?
- What organelle are the short, hair-like structures that cover some cells & help them move known as?
- State the 3 parts of the Cell Theory.
 Does water move into, out of, or are they at equilibrium in the cell shown above?
Does water move into, out of, or are they at equilibrium in the cell shown above?- What term means the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane?
- The cell organelle that makes energy available for the cell is the __?__.
- In a cell, the jelly-like area between the nucleus and the cell membrane is known as the __?__.
- The part of the cell that controls what enters & leaves the cell is the __?__.
- Which term includes the other three? A) nucleolus, B) organelle, C) rough ER, D) chloroplast.
- List 2 ways that a plant cell is different from animal cells.
- List 2 ways that an animal cell is different from plant cells.
- Are primitive cells that lack a nucleus said to be examples of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells?
- State the Fluid Mosaic Model Theory of plasma membranes.
- List 2 examples of cell types that are prokaryotic.
- What does it mean if a solution is isotonic?
- What does it mean if a solution is hypertonic?
- What does it mean if a solution is hypotonic?
- List 3 different kinds of organisms that have cells that are classified as eukaryotic.
- How many micrometers are found in 1 mm?
- What type of passive transport involves the carrying of large molecules like glucose across a membrane by a protein from high concentration to low concentration?
- What type of active transport involves the movement of glucose, sucrose or amino acids into a cell from low to high concentration in conjunction with the movement of ions into the cell that are provided by a Na-K pump or proton pump?
- List 2 eukaryotic cell organelles that contain DNA besides the nucleus.
- List 2 ways that the DNA of prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells is different.
 Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution?
Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution? Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution?
Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution? Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution?
Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution? What cell structure is shown at left?
What cell structure is shown at left? What part of a phospholipids is shown by B? State whether it is hydrophobic or hydrophyllic.
What part of a phospholipids is shown by B? State whether it is hydrophobic or hydrophyllic. What special term describes the plasma membrane shown at left.
What special term describes the plasma membrane shown at left. What part of a phospholipids is shown by A? State whether it is hydrophobic or hydrophyllic.
What part of a phospholipids is shown by A? State whether it is hydrophobic or hydrophyllic.- State the The Theory of Endosymbiosis.
- State the Fluid Mosaid Model Theory of plasma membnranes.
- State what cell differentiation means.
- How many µm would 0.076 mm be equivalent to?
- List 2 ways that prokaryotic cells are different from eukaryotic cells.
- List one reason why cells remain small……..ie, they never get very large in size.
- What part of a phospholipids is “water fearing”?
- What part of a phospholipids is “water loving”?
- List the name of the molecule that is found occasionally throughout plasma membrane that helps make the membrane more fluid.
- In which cell organelle does lipid and carbohydrate synthesis occur in?
- Name at least one cellular organelle that contains DNA (in eukaryotic cells).
- Which organelle of eukaryotic cells manufactures complex lipids and carbohydrates?
- What is the function of the mesosome of prokaryotic cells?
- What is the special scientific name for the membrane found around prokaryotic cells?
- What structure is found outside the plasma membrane of plant cells, is made of the carbo known as cellulose, and provides support and structure for the plant cell?
- List 3 ways that plant cells are different from animal cells.
- What does the term hydrophyllic literally mean?
- What does the term hydrophobic literally mean?
Slichter
 What name is given to the stringy organelles that contain DNA in the cell nucleus?
What name is given to the stringy organelles that contain DNA in the cell nucleus? What is the outer edge of a cell called? (This is an animal cell.)
What is the outer edge of a cell called? (This is an animal cell.) What part of the cell is this? (the whole circular area)
What part of the cell is this? (the whole circular area) What part of the cell is this dark dot?
What part of the cell is this dark dot? What part of the cell is this?
What part of the cell is this? What term is given to the tiny round dots found in rough ER that are used to make proteins?
What term is given to the tiny round dots found in rough ER that are used to make proteins? What are these cellular tubes called?
What are these cellular tubes called? What are these 2 clear circular storage areas of a cell called?
What are these 2 clear circular storage areas of a cell called? What is the outer surface of this cell structure known as?
What is the outer surface of this cell structure known as?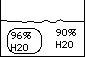 Will water flow into, out of the cell, or are they at equilibrium?
Will water flow into, out of the cell, or are they at equilibrium? Will water flow into, out of, or are they in equilibrium in the cell?
Will water flow into, out of, or are they in equilibrium in the cell? Does water move into, out of, or are they at equilibrium in the cell shown above?
Does water move into, out of, or are they at equilibrium in the cell shown above? Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution?
Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution? Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution?
Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution? Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution?
Is the cytoplasm of the cell at left, hypotonic, or hypertonic to the surrounding solution? What cell structure is shown at left?
What cell structure is shown at left? What part of a phospholipids is shown by B? State whether it is hydrophobic or hydrophyllic.
What part of a phospholipids is shown by B? State whether it is hydrophobic or hydrophyllic. What special term describes the plasma membrane shown at left.
What special term describes the plasma membrane shown at left. What part of a phospholipids is shown by A? State whether it is hydrophobic or hydrophyllic.
What part of a phospholipids is shown by A? State whether it is hydrophobic or hydrophyllic.