(More Advanced Version)
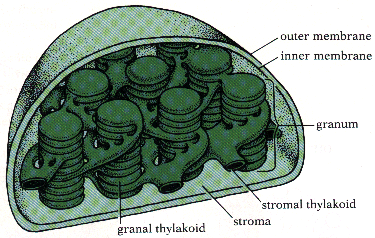
(More Advanced Version)

1. Light Dependent Reactions (LDR) - Needs light to occur. Makes ATP, NADPH, O2.
2. Light Independent Reactions (LIR) - May occur in light or dark. Converts CO2 to sugars.
The ATP & NADPH accumulate & diffuse to the stroma where they are used to make sugar.
ATP is a short-term energy carrier & main energy source for all cells.
NADPH is a short-term energy carrier & also carries electrons & H+ ions from the breakdown of water.
Plant pigments are organized as photosystems (Pigments surrounding a central chlorophyll a molecule....the reaction center).
Each pigment absorbs a different wavelength of light & transfers its energy to the reaction center which in turns energizes an electron.
Only the chlorphyll that is the reaction center can give the energized electrons to the electron acceptors!
The energized electron is then used elsewhere to make ATP or NADPH.
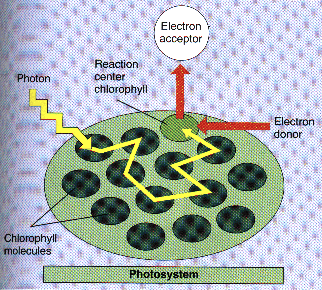
Photosystem I (PS I) - Part of the LDR where chlorophyll is energized a 2nd time to make 2 NADPH. The reaction center of PS I uses light energy of 700 nm.
Photosystem II (PS II) - Part of the LDR where photolysis occurs and chemiosmosis makes ATP via photophosphorylation. The reaction center of PS II uses light energy of 680 nm.
A. Cyclic Photophosphorylation: Excited electrons are cycled through a series of electron acceptors to make ATP.
B. Noncyclic Photophosphorylation:
a. Light energizes chlorophyll, which splits H2O (photolysis). The O2 is released to air.
b. More light energizes another chlorophyll which releases energy to make 2 ATP.
c. A different wavelength of light energizes another chlorophyll, which then releases energy to make 2 NADPH.
Photophosphorylation: Use of light energy in LDR to make ATP.
Chemiosmosis: Use of H+ gradient (high to low) to create ATP during LDR. Hydrogen pump transports H+ into the thylakoid. H+ also made by photolysis. H+ diffuses through thylakoid membrane via protein channel.
ATP Synthase takes energy from the flow of protons & gives it to ADP & P to make ATP.