
(Notes for your handout are shown in blue text on the diagram above!)
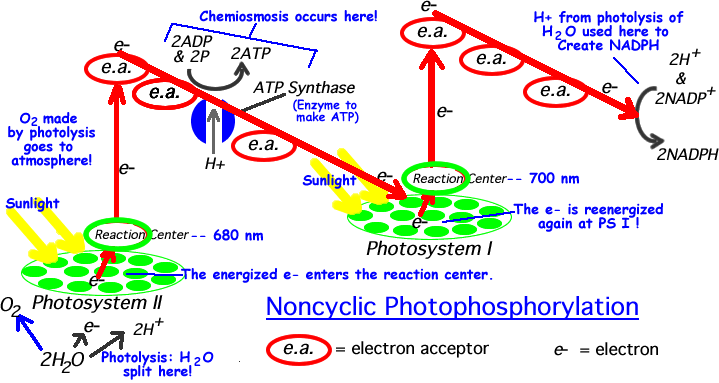
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation produces ATP using the energy from excited electrons provided by photosystem II.
As electrons pass through the non-cyclic pathway, they do not return to the original photosystem. This does not create a cycle, hence the name non-cyclic.
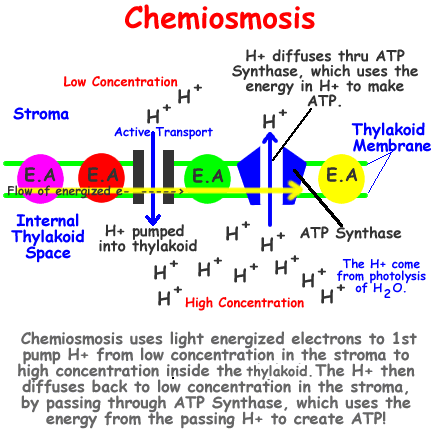
1. Photolysis provides H+ ions to replace those lost in the photosystems. The excited electrons provide energy for a proton pump to actively transport additional H+ into the thylakoid. The high concentration of H+ diffuse past ATP synthase as they pass out of the membrane to the lower H+ concentration. The energy created as H+ passes the ATP synthase forms ATP.
Diffusion of H+ ions from high to low concentration through ATP synthase to form ATP is called chemiosmosis.
2. The electrons provided by non-cyclic photophosphorylation are boosted a 2nd time to a higher energy level by photosystem I to then create 2 NADPH.