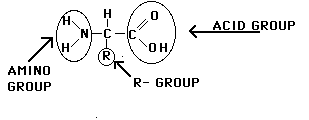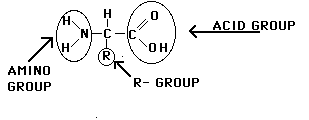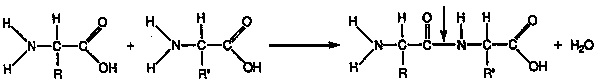CHEMICALS OF LIFE:
1. WATER
2. CARBON BASED (ORGANIC) COMPOUNDS
ORGANIC MOLECULES
Carbon atoms bonded to at least 1 hydrogen
atom. Frequently bonded to oxygen or other carbon atoms. Carbon is a
unique element due to its ability to form covalent bonds that are strong and
stable.
Subunit molecules: Small organic
molecules (building blocks).
Macromolecules (macro = large).
Several subunits are bonded together to make larger molecules.
TYPES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS:
A. Proteins
PROTEINS
Large molecules that are made up of many amino acids bonded
together in long chains. Proteins make up structures in cells. >50% of dry body
wt..
Other importances:
a) Enzymes
b) hormones
c) contractile fibers of muscles
d) O2 transport
e) toxins (poisons)
1. AMINO ACIDS: Building blocks
of all proteins. 20 types. All contain carboxyl group (COOH), amino group (NH2),
& R group (variable). R group is the only difference for each amino acid.
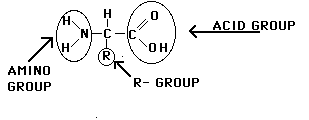
2. Dipeptide: 2 amino acids linked
together.
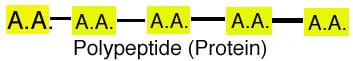
3. Polypeptides (3 or more amino
acids bonded together). Peptide bond connects 2 a.a.s together. Peptide bond
occurs between carboxyl group of one a.a. & amino group of 2nd a.a..
DEHYDRATION: Reaction to form a peptide bond, where H2O is released
as bond forms.
aa + aa ----> protein + H20
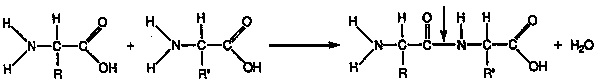
Slichter