CARBOHYDRATES
Carbohydrates include all sugars, almost a (CH2O)n 1:2:1 ratio
of C:H:O.
Carbohydrate Subunits: Monosaccharides
(simple sugars)-------
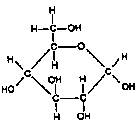
All have formula C6H12O6. Examples: Glucose (shown above) & Fructose
Macromolecule Carbos:
A. Disaccharides (double sugars,
m-m) Ex.- Table Sugar (sucrose).-
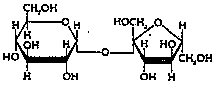
B. Polysaccharides (“many” sugars, m-m-m-)
--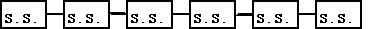
Types of polysaccharides:
a. Glycogen: Animal energy storage found in our liver.
b. Starch: Plant energy storage.
c. Cellulose: wood. Most abundant carbo.
Importance of Carbohydrates:
1. Glucose- key fuel of all cells.
2. Glycogen- long term energy storage for animal cells (stores the glucose
molecules in a form not easily used!).
3. Plant Starch- long term energy storage for plant cells (stores the glucose
molecules in a form that is not easily used!)
4. Cellulose- Sturdy structural carbo.. of cell walls. Makes wood.
Slichter
