Internal Structure
of the Rootof a Typical
Dicotyledonous Plant
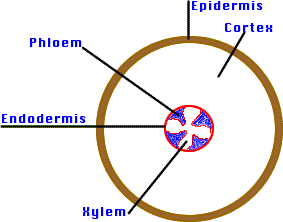
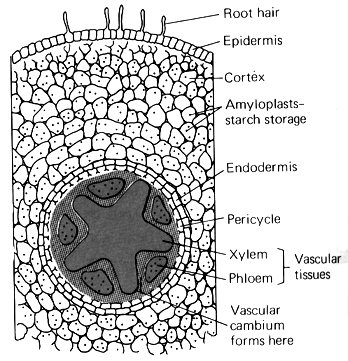
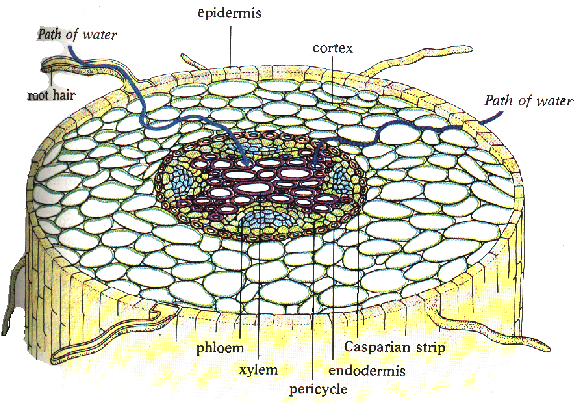
Root structure:
a) Epidermis: Outer layer of cells
("skin"). Protection.
b) Root Hair: An extension of specialized
root epidermal cells increasing surface area for absorption of water & minerals.
c) Cortex: Region between epidermis
& vascular cylinder. Supports plant parts & stores food.
d) Endodermis: Layer of cells just
outside vascular cylinder.
e)Pericycle: Cylindrical layer of
cells inside endodermis. Origin of cork & secondary (side) roots.
f) Vascular Cylinder: Arrangement
of vascular tissues as a central cylinder in roots. This is shown as the large
circular area in the middle of both diagrams.
g) Xylem: Living (outer) vascular
system carrying water & minerals throughout plant.
h) Phloem: Living (inner) vascular
system carrying dissolved sugars and organic compounds throughout plant.
Note:The diagrams that students will draw should show zones or
general regions. Individual cells need not be illustrated.
Slichter