 Only 1 side of DNA in a gene gets transcribed:
Only 1 side of DNA in a gene gets transcribed:Chapter 15
1. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): make up ribosomes & involved in translation. Produced in nucleolus.
2. Transfer RNA (tRNA): transport amino acids to ribosomes.
3. Messenger RNA (mRNA): copied from DNA, conveys information from chromosomes to ribosomes
Transcription: Process that converts DNA code of a gene into mRNA code.
Gene: Section of DNA within a chromosome that codes for the synthesis of one protein. There are roughly 20-30,000 genes on the 23 pairs of human chromosomes.
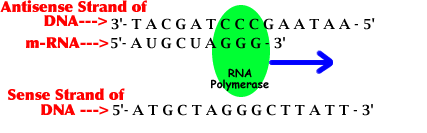
 Only 1 side of DNA in a gene gets transcribed:
Only 1 side of DNA in a gene gets transcribed:
A. Sense Strand: Strand of DNA in a gene which has the same nucleotide sequence as the m-RNA (except with T instead of U).
B. Antisense Strand: Strand of DNA that is transcribed to create m-RNA. It is the template used for making m-RNA.
RNA polymerase: enzyme that initiates transcription by binding to promoter (TAC code on DNA). RNA polymerase reads the Antisense DNA Strand from 3'--->5'.
Promoter site: sequences in the DNA strand (TAC) which accept RNA polymerase and begin transcription
Elongation: mRNA bonds with DNA in small units, transcription bubble, adding bases Adenine to uracil & Guanine to cytosine, etc.. in the 5' to 3' direction (on the new m-RNA).
Termination: terminator or stop signal disengages RNA polymerase to end transcription.
Codon: sequence of 3 nucleotides on m-RNA that codes for one amino acid. Each amino acid has one to several different codons.
A Site with a good beginning Animation of Transcription (Needs Shockwave)
Much of DNA is non-coding nucleotide base sequences, not genes
Intron: part of gene (DNA or mRNA) that does not code for proteins. It must be removed before mRNA is exported to the ribosome.
Exon: coding part of DNA (or mRNA). The exon is what is translated at the ribosome during protein synthesis.