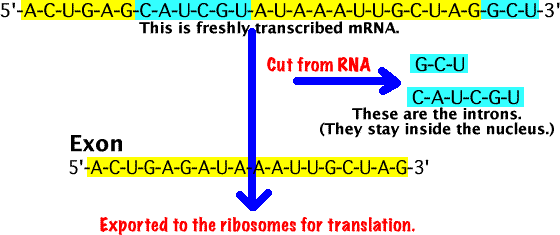

Transcription copies the DNA code of a gene and converts it to messenger RNA (m RNA). The m RNA will be used at the ribosome to make polypeptides (proteins). However all of the code contained in the m RNA molecule is not needed to produce the polypeptide. The sections of m RNA which do not code for translation of a polypeptide are called introns. As the m RNA readies itself to leave the nucleus, enzymes cut out and remove the introns. The remaining mRNA sections are spliced back together again by a different enzyme. This modified m RNA is known as an exon and is what comes to the ribosome to be translated into polypeptides.
Introns: Sections of mRNA not needed to produce a protein. These are cut out of the mRNA and kept in the nucleus.
Exons: Sections of mRNA containing the code to synthesize a protein. These are exported from the nucleus and proceed to the ribosome where they are used to synthesize the protein.