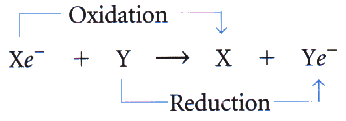
Oxidation vs. Reduction Reactions
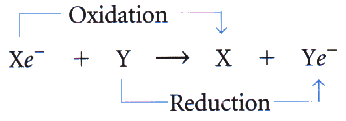
|
Oxidation Reactions
|
Reduction Reactions
|
| Adding oxygen atoms to a substance. | Removing oxygen atoms from a substance. |
| Loss of electrons from a substance. | Adding electrons to a substance. |
| Loss of hydrogen atoms from a substance. | Addition of hydrogen atoms to a substance. |
| The substance loses energy when it loses electrons & hydrogen atoms. | The substance gaining electrons or hydrogen atoms gains energy. |
As a result of oxidation reactions in living cells, hydrogen atoms tend to carry electrons and energy to the substance to be reduced.
Example #1:
![]()
NAD+ is reduced to NADH by addition of 1H and 1 electron from the 2nd H.
The 2nd H is oxidized to H+ by the loss of an electron.
Example #2:
Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP ----> 2 Pyruvate + 2NADH + 2ATP
Glucose is oxidized to pyruvate by loss of both electrons and hydrogen atoms.
NAD is reduced to NADH by addition of both hydrogen atoms and electrons.
ADP is reduced to ATP by addition of electrons.
Glucose has lost energy and 2 hydrogen atoms as a result.
NADH and ATP both gain energy (Both are energy carriers.).
Slichter