Krebs Cycle
a) Krebs cycle ccurs in matrix.
b) Only occurs if O2 present.
c) Link Reaction: Pyruvate moves into matrix & reacts with coenzyme A (CoA) (via oxidative decarboxylation) to form Acetyl-CoA (2C). 1 CO2 & 1 NADH are released by this reaction.
Oxidative decarboxylation means the pyruvate is oxidized (by removal of H) & decarboxylated by removal of CO2.
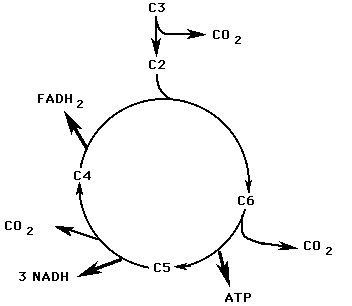
The diagram below is a very simple outline of the Krebs Cycle showing the removal of CO2, and the synthesis of 3 NADH, 1FADH2, and 1 ATP. Its purpose is to visualize in simple form, what occurs during the Krebs Cycle. The locations where molecules are removed are not necessarily always accurate.

[More Complex Diagram of Krebs Cycle]
|
Summary of One Turn of the Krebs
Cycle
|
| 1. Acetyl CoA (2C) enters the cycle & joins a 4C molecule. |
| 2. In a series of steps, the remaining H and high energy electrons are removed from the Acetyl CoA. |
| 3. Three NAD+ are converted into 3 NADH & 3H+. |
| 4. One FAD is converted into 1 FADH2. |
| 5. One ATP is made (by substrate phosphorylation). |
| 6. Two CO2 are released. |
| 7. At the end of the cycle, nothing remains of the original glucose molecule. |
During the Krebs cycle, addition of a phosphate to ADP to make ATP is known as substrate-level phosphorylation.
[Glycolysis] [Electron Transport]
Slichter