Cell Respiration: Controlled release of energy from organic molecules (most often glucose) by oxidation in order to generate ATP.

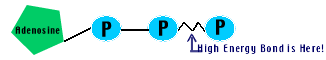
ATP: Adenosine TriPhosphate - Energy carrying molecule. Carries measured doses of energy. Used to facillitate many cell reactions.
![]()
NADH: A second energy carrying molecule in the mitochondria. NADH is a coenzyme.
![]()
FADH2: A third energy carrying molecule in the mitochondria. FADH2 is also a coenzyme.
Coenzymes are nucleotides (like A, T, C or G) which act as enzyme helpers. They accept hydrogen and electrons from substrates at one reaction site transfer them to a second reaction site. Adenine (A) is the nucleotide found in both NADH and FADH2.
a. Krebs Cycle
b. Krebs Cycle Diagram
c. Electron Transport / Oxidative Phosphorylation
a. Fats converted to fatty acids & glycerol by digestion.
b. Glycerol converted to pyruvate.
c. Fatty Acids converted to Acetyl-CoA.
d. Both fat parts can then be used in Kreb's cycle.