1. Glycolysis
2. Krebs Cycle
3. Electron Transport
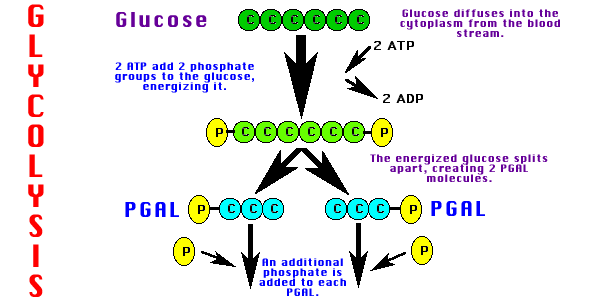
Glycolysis is the first series of reactions that break glucose apart to liberate the energy it holds in its covalent chemical bonds. Glycolysis occurs in both aerobic (with oxygen) and anerobic (does not need oxygen) respiration!
Glycolysis basically:
a) splits Glucose (6 C) to make two 3-carbon molecules. 2 ATP needed to split glucose.
b) removes energy and hydrogen from the 3-carbon molecules. This is used to make NADH (E. carrier).
c) removes more energy to make 4 ATP. 2 ATP go to split next glucose. 2 ATP available for cell use.
d) At end of glycolysis, 2 pyruvate molecules (3C) left.

|
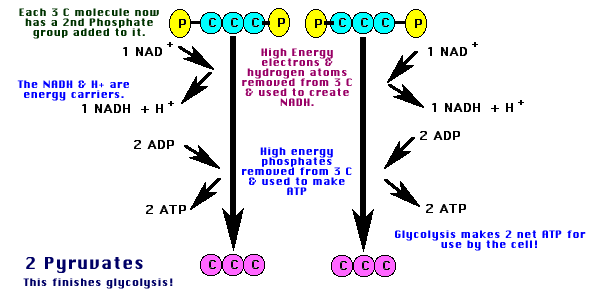
Summary of Glycolysis
|
| 1. One glucose (6C) converted into 2 pyruvates (3C). |
| 2. Net yield of 2 ATP for use by cell. |
| 3. Two NAD+ are converted into 2 NADH & 2H+. (These go to Electron Transport.) |
[Anaerobic Respiration (Fermentation)] [Aerobic Respiration]
Slichter