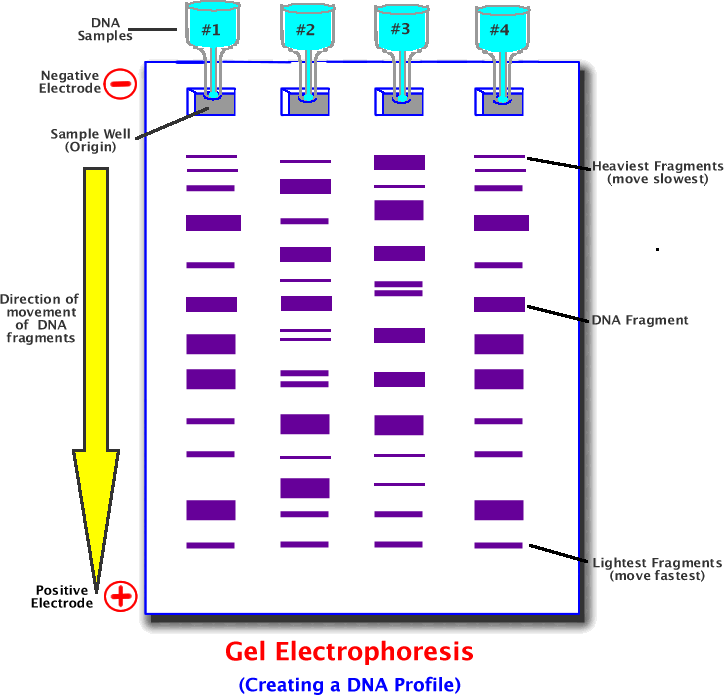
Gel electrophoresis is a process used to separate molecules based upon their charge and mass using an electric field. This process is commonly used to separated sections of DNA cut using restriction enzymes to create what many of us would call a DNA fingerprint.
1) DNA is cut into smaller fragments using restriction enzymes.
2) The cut DNA is placed into small holes in a piece of gelatin (the holes are called origins).
3) Electrodes are hooked to both ends of the gel.
4) Electrical current runs through the gel, carrying the DNA fragments towards the far end. Small DNA fragments move faster as they are lighter. Large DNA fragments move slower as they are heavier.
5) At the end of electrophoresis, the gel is treated with a dye so the DNA bands become visible.
a) Forensic (crime scene) investigations
b) Paternity (who is the legal father of a child)
c) Identity of unknown persons or bodies
d) Evolutionary studies (compare DNA profiles to see what organisms are more closely related)