Introduction to Genetics:
Read pp 117-122 in your books!
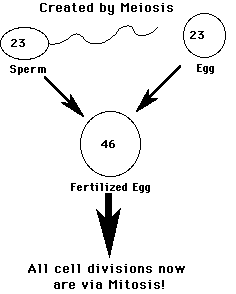
Remember that Meiosis is sexual reproduction, wherein special
sex cells within the ovaries or testes first double their chromosome number
(from 46 to 92), then in a series of two divisions, create eggs or sperm with
one-half the normal chromosome number (23).
Genetics- Study of how traits are inherited or
passed between generations.
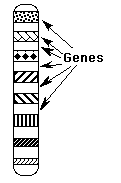 Chromosomes-
Part of cell nucleus that controls what the cell does, & thus controls all
your traits. Humans = 46 chromosomes.
Chromosomes-
Part of cell nucleus that controls what the cell does, & thus controls all
your traits. Humans = 46 chromosomes.
Genes- Small sections of chromosome that are
responsible for making 1 trait. Each person has at least 1 pair of genes (1
from mom, 1 from dad) for each trait.
The gene pairs are called alleles.
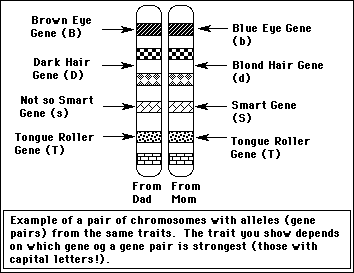
Dominant Gene- The stronger gene of a gene pair.
Shown by a capital letter (A, T, E, R......)
Recessive Gene- The weaker gene of a gene pair.
Shown by a lower case letter (a, t, w, r.....). If a person has both a dominant
& recessive gene, the recessive one isn't seen. For a person to see a recessive
trait, the person must have 2 recessive genes in the gene pair (Ex....aa, tt,
ww, rr...).
Homozygous- Both alleles (genes) of gene pair
are identical. AA, tt, yy, BB, nn......
Heterozygous- Both alleles (genes) of gene pair
are different. Aa, Tt, Yy, Bb, Nn.......The dominant (big letter) allele wins
out & is shown.
Genotype- The 2 "gene" or allele letters
a person has for a trait. Examples: AA, Tt, rr, Ww, ii, QQ.
Phenotype- What the trait looks like (blue eyes,
brown eyes, black hair, blonde hair, light skin, dark skin, etc....)
Slichter


 Chromosomes-
Part of cell nucleus that controls what the cell does, & thus controls all
your traits. Humans = 46 chromosomes.
Chromosomes-
Part of cell nucleus that controls what the cell does, & thus controls all
your traits. Humans = 46 chromosomes.