Cellular Respiration: is the process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen.
Cellular Respiration = Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria.
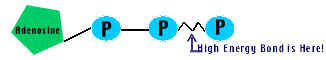
Some of the energy released by breaking food down is stored as ATP, while some is released as heat.
ATP is a short-term energy storage molecule all cells use as their energy source.

![]()
Reactants of Cellular Respiration:
Glucose (C6H12O6) & Oxygen (O2)
Products of Cellular Respiration:
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) & Water (H2O) & ATP & Heat
Anaerobic Respiration: (Fermentation) Respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen to still make some ATP to keep cells alive.
2 Kinds of Anaerobic Respiration:
a) Lactic Acid Fermentation - (Occurs in muscle cells for short periods of time!) Breaks sugar down to Lactic acid + 2ATP.
b) Alcohol Fermentation - (Occurs in yeast & some bacteria) Breaks sugar down to Alcohol + CO2 + 2ATP.