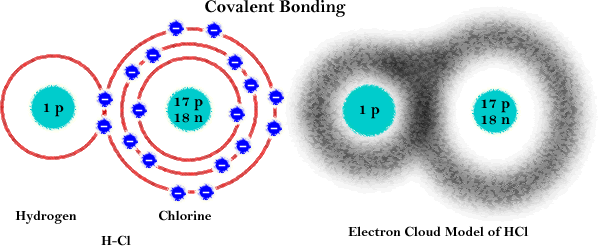
Covalent Bond: Strong chemical bond where two atoms share electrons so both can achieve full outer orbits.

Ionic Bond: Weak chemical bond where two atoms achieve full outer orbits when one atom takes electrons from the other. The result is one atom becomes negatively charged (the one gaining the electron/s) & the other becomes positively charged (the one losing the electron/s).
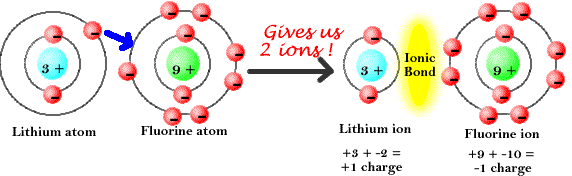
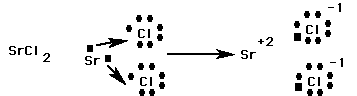
Negative Ion: Atom that gains electrons. Resulting atom has more electrons than protons. Elements in rows 5-7 may become negative ions.
Water is a molecule with covalent bonds between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms. However, oxygen has a high tendency to steal electrons from other atoms, so water occasionally becomes ionized.
H20 --------> H+ + OH-.
Acid:
Any substance having more H+ ions than OH- ions.
Base: Any substance having more OH- ions than H+
ions.
pH: System used to measure the number of hydrogen
ions (H+) in a substance. It is a logorithmic math scale.
pH of 1-6.9 ----- Acid. -----
H+ > OH- ("Stings" in cuts, burns below pH=4)
pH of 7.0 ----- Neutral ----- H+ = OH-
pH of 7.1-14 ----- Base ----- OH- > H+ (Feels slippery, burns above pH=10)