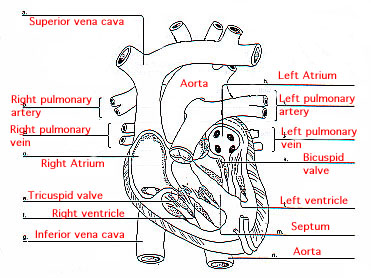
 Heart
: Muscular pump with 4 chambers, contracting at regular intervals to force blood
through the circulatory system.
Heart
: Muscular pump with 4 chambers, contracting at regular intervals to force blood
through the circulatory system.Left side of heart receives & pumps oxygen rich blood from lungs.
Left Atrium : Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary
vein. Pumps blood to left ventricle.
Left Ventricle : Pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta & hence to all
body cells (except lungs).
Septum : Thick wall that separates the left & right chambers of the
heart.
Right side of heart receives & pumps oxygen poor blood.
Right Atrium : Receives oxygen poor blood from the body via the upper
& lower vena cavas. Sends blood to right ventricle.
Right Ventricle : Pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs.
Valve : Valves (like trap doors) between the atria and ventricles which
allow flow into the ventricles, but no flow backwards to atria.
Pacemaker : (Sinoatrial node) Nerve tissues that receive impulses from
brain or spinal column & transfer signal to heart. Controls heart beat.
Found atop right atrium.
Vena Cava (superior & inferior): Large veins collecting oxygen poor
blood from smaller veins in body. Superior v.c. brings blood from upper body,
inferior v.c. brings blood from the lower body.
Aorta : Large, thick muscled artery through which oxygenated blood
leaves the heart (from left ventricle) for the body tissues.
Pulmonary Artery : Artery transporting oxygen poor blood from right
ventricle to lungs.
Pulmonary Vein : Vein transporting oxygen rich blood from lungs to
left atrium.
Artery : Transports blood outward from heart to all body tissues. Must
be thick, muscular & elastic to withstand pressure from heartbeat.
Capillary : Thin blood vessels in the tissues (about one red blood
cell wide) through which oxygen & nutrients diffuse to the cells, and wastes
& CO2 diffuse into the blood. Found between all arteries & veins.
Vein : Blood vessels carrying blood towards the heart from body tissues
or organs. Are thin-walled as blood pressure is low.