Internal Structure of the Leaf
of a Typical Dicotyledonous Plant
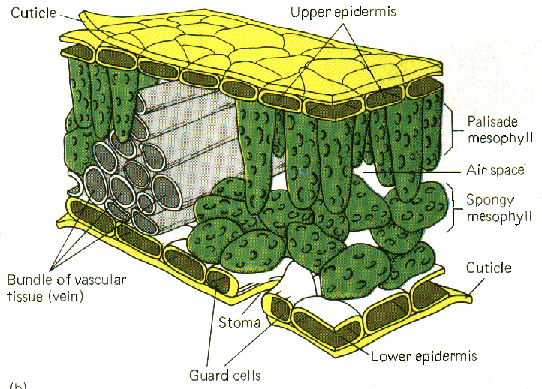
Internal Leaf Structure
a) Cuticle: Waxy layer water proofing
upper leaves.
b) Upper epidermis: Upper layer
of cells. No chloroplasts. Protection.
c) Palisade Mesophyll: Tightly
packed upper layer of chloroplast containing cells.
d) Spongy Mesophyll: Lower layer
of chloroplast containing cells. Air spaces around them.
e) Lower Epidermis: Lower external
layer of cells in leaf.
f) Vascular Bundle: Bundle of
many vessels (xylem and phloem) for transport.
g) Xylem: Living vascular system
carrying water & minerals throughout plant.
h) Phloem: Living vascular system
carrying dissolved sugars and organic compounds throughout plant.
i) Guard Cells: 2 cells surrounding
stomata that control rate of gas & water exchange.
j) Stomata: Opening between guard
cells for gas & water exchange. (See Diagram below.)
Long
& Slichter

