Theoretical Genetics
Terminology
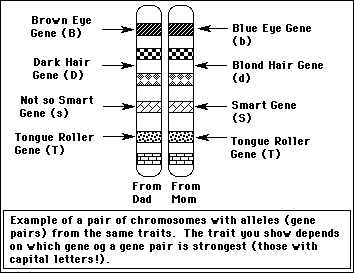
Allele: One gene of a gene pair for a trait.
In the gene pair Bb for hair color, both B & b are alleles .
Genotype: The 2 alleles an organism possesses
for a trait. (Its genetic makeup.)
Phenotype: The external appearance of the organism
for a trait. (blue eyes, black hair, hitchhiker's thumb, etc...)
Dominant Allele: An allele that masks the presence
of another allele for the same characteristic. Usually shown as a capital letter
(Ex......A, B, G, T, etc....)
Recessive Allele: An allele that is hidden by
the presence of a dominant allele for the same characteristic. Usually shown
as a lower case letter (Ex......a, b, c, t, etc....)
Example:
(In eye color, brown eyes (B) is dominant to blue eyes (b). Individuals who
are Bb have brown eyes. Blue eyed people can only be bb.)
Codominant Alleles: Pairs of alleles that both
affect the phenotype (appearance) of the individual. Neither allele is completely
dominant.
Example: In hair, straight hair (S) is codominant
to curly hair (s). Individuals with the genotype Ss show the effects of both
traits, and thus have wavy hair.
Locus: The particular position on a chromosome
where a gene is.
Homozygous: Having 2 identical alleles of a gene
(Ex: AA, bb, DD.....)
Heterozygous: Having 2 different alleles of a
gene (Ex: Aa, Bb, Dd.....)
Carrier: an individual that has a recessive alele
of a gene that does not have an effect on their phenotype.
Test cross: Testing a suspected heterozygote
by crossing it with a known homozygous recessive.
Slichter

