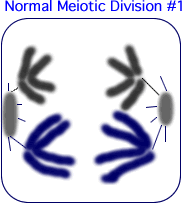
 -------------
------------- 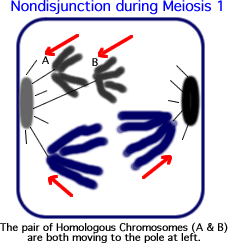 -------------
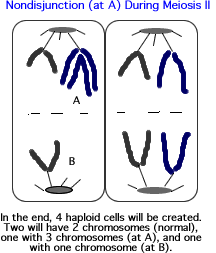
------------- 
Non-disjunction
Non-disjunction occurs when chromosomes in the developing gamete (sex cell) fail to separate during one of the divisions of meiosis. The result is a sperm or egg cell with either an additional chromosome, or one that lacks one chromosome. When this sex cell combines with one from the opposite sex, the resulting fetus will have cells with an extra, or one chromosome that is lacking. Generally, such fetus' will not develop properly and we would say that the resulting baby would have a birth defect. However, be aware that not all birth defects are caused by non-disjunction.
 -------------
-------------  -------------
------------- 
Examples of Nondisjunction:
A. Down's Syndrome: 47 chromosomes with 3 #21 chromosomes.
B. Triple-X Syndrome: 47 chromosomes caused by 3 X chromosomes.
C. Klinefelter's Syndrome: 47 chromosomes caused by 2 X chromosomes and 1 Y chromosomes.
D. Turner's Syndrome: 45 chromosomes with 1 X chromosome (caused by the absence of one of the X chromosomes or a Y chromosome).
Slichter