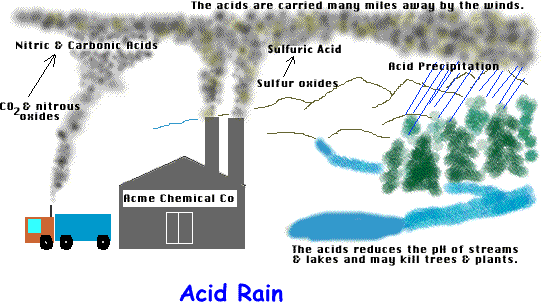
(Acid Precipitation)

Any precipitation carrying dissolved acids from natural or man made causes.
Examples;
a. CO2 dissolves in H2O---------> Creates carbonic acid (H2CO3)
b. Sulfur dioxide (from internal combustion) mixes with H2O ---------> Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4)
c. Nitogen oxides (from internal combustion) mixes with H2O ---------> Nitric Acid (HNO3)
*Acid precipitation may have a pH as low as 3. Very Acidic!
*Acids in the air may be carried thousands of miles from their source, polluting soil & water in pristine areas!
a) Trees (especially conifers) sensitive to low pH. Causes death of leaves, weakening trees.
b) Fish & aquatic insects sensitive to changes in pH. Causes death & disruption of food chains.
c) Minerals (K+, Mg+2, & Ca+2) leached from soil, making soil less fertile
d) Acidic H2O leaches Aluminum from soil. Aluminum ions toxic to fish & aquatic insects.
a) Require catalytic converters on auto & truck engines & factory smoke stacks.
b) Require that all chemical wastes be neutralized before disposal.
c) Convert to hydrogen fuels, solar or wind for energy.
Acid Precipitation (EPA)
Acid Rain (Rice University)