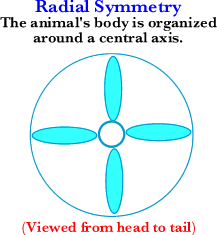
Radial Symmetry: Body plan in which parts of an animal's body are organized in a circle around a central axis. (Can be cut into identical halves in 2 or more planes.)
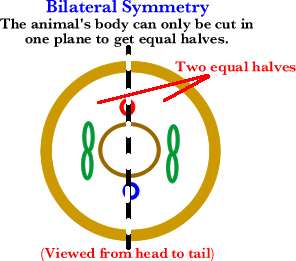
Bilateral Symmetry: Body plan in which two equal halves of a body mirror each other. (Has left and right sides.)
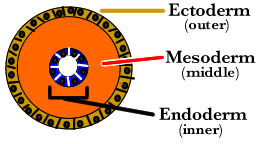
Ectoderm: Outer layer of cells giving rise to skin, nervous system, and external sensory organs.
Mesoderm: Middle layer of cells giving rise to muscles, blood and various systems.
Endoderm: Innermost layer of cells giving rise to linings of the digestive tract, bladder, urinary tract, respiratory tract.
Additional Online Info: http://biology.clc.uc.edu/Courses/bio106/inverts.htm
| Phyla | Examples | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Porifera | Sponges | 1) Lack all organs. 2) No Symmetry. 3) Body wall with by pores thru which water enters. 4) Needle-like spicules provide support & protection. 5) Body wall of 2 layers (ectoderm & endoderm), each separated by a thin jelly layer. |
Cnidaria (jelly animals) |
1) Radial Symmetry. 2) Has digestive and nervous systems. 3) Single opening acts as mouth and anus. 4) Tentacles have stinging cells (nematocysts). 5) Body wall of 2 layers (ectoderm & endoderm), each separated by jelly layer. 6) 2 basic body forms:
|
|
Platyhelminthes (flatworms) |
1) Bilateral Symmetry (flattened bodies top to bottom) 2) Unsegmented bodies. 3) Have digestive and nervous systems. 4) Have mouth but no anus. 5) Body wall of 3 layers (ectoderm, mesoderm & endoderm). |
|
Annelida (segmented worms) |
1) Bilateral Symmetry 2) Cylindrical, segmented bodies. 3) Bristles or appendages on each body segment aid movement or sensory input. 4) Digestive system is one-way (mouth to anus). 5) Has nervous, excretory & circulatory systems. 6) Body wall of 3 layers (ectoderm, mesoderm & endoderm). |
|
| Mollusca | 1) Soft, unsegmented bodies. 2) Body made of head, muscular foot, and organs (all). 3) Most with hard external shell (except slug, squid, octopi). 4) Most have radula (rasping tongue) - (except bivalves). 5) Body wall of 3 layers (ectoderm, mesoderm & endoderm). |
|
| Arthropoda | Crustaceans (crabs, shrimp, pill bugs) Arachnids (spiders & scorpions) |
1) Jointed legs. 2) Exoskeleton of chitin (external). 3) Body segmentation. 4) Compound eyes. 5) Body wall of 3 layers (ectoderm, mesoderm & endoderm). 6) One-way digestive system. |
[Review of Simple Animal Phyla]