CARBOHYDRATES
Carbohydrates include all sugars, almost a (CH2O)n 1:2:1 ratio
of C:H:O.
Monomer Carbos: Monosaccharides (simple sugars)-------
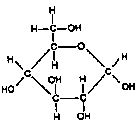
All have formula C6H12O6. Examples: Glucose (shown above) & Fructose
Polymer Carbos:
A. Disaccharides (double sugars, m-m) Ex.- Table Sugar (sucrose).---
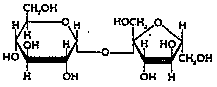
B. Polysaccharides (“many” sugars, m-m-m-) --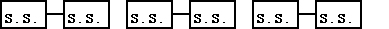
Types of polysaccharides:
a. Glycogen: Animal energy storage found in our liver.
b. Starch: Plant energy storage.
c. Cellulose: Plant building material (wood). Most abundant carbo.
Lipids
*Organic molecules not dissolvable in H2O.
*Major part of cell membranes.
*Lipids contain many C-H bonds which store energy.
All Lipids are monomers.
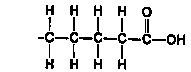
Most contain fatty acids, long chains of C-H bonds ending in COOH, which are
then bonded to Glycerol.
Saturated Fatty Acid (F.A.)- all bonds are C-C
or C-H. Contains more energy, thus more fattening.
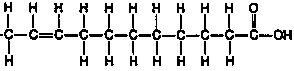
Unsaturated F.A.- some bonds may be C=C. Contains
less energy, less fattening.
Types of Lipids:
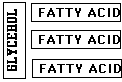
A. Triglycerides: Made of glycerol & 3 fatty
acids. (EX. Fats & oils)
 ---or---
---or---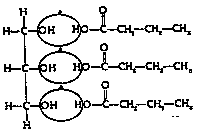
B. Phospholipids: Glycerol, 2 fatty acids,
& 1 phosphate group (PO4). (Ex.-Cell membranes)
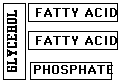 ------or---
------or---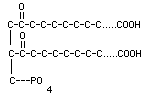
C. Wax: Fatty Acid & an alcohol group (OH).
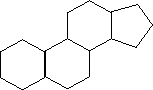
D. Steroids: Consist of four 5- or 6-sided
carbon rings joined together. Has no fatty acids. (Ex.- Cholesterol, hormones)
Nucleic Acids
Largest molecules made by organisms. They store the info a cell needs to
make proteins
1. DNA- Genetic material. Template for all
proteins. Controls RNA.
2. RNA- Smaller genetic material. Directs
protein synthesis.
Nucleic acids contain both nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) which helps to
identify them.
The diagram below illustrates a nucleotide, which is the monomer (building
block form of all nucleic acids).

Slichter



---or---
------or---