[-------------- DNA & RNA Code
of Life
Homework - Read Pages 141-145
Gene: A small piece of DNA that
has a code to make one protein, and thus one trait.
Examples:
Blue eyed gene codes to make blue eye protein.
Black hair gene codes to make a protein that makes hair black.......
Genes and DNA canŐt move out of the nucleus, so RNA is used to carry the message
out.
RNA: similar to DNA, except that
the base T is replaced by base U. RNA uses the DNA code to make proteins.
 A.
messenger-RNA: (m-RNA) copies the DNA code of a gene to carry
out of nucleus.
A.
messenger-RNA: (m-RNA) copies the DNA code of a gene to carry
out of nucleus.
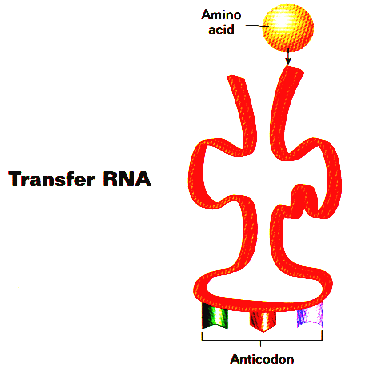
B. transfer-RNA:
(t-RNA) type of RNA that carries one specific amino acid to the ribosome to
help make proteins. A t-RNA molecule is shown at right.
Triplet: The genetic code on DNA
for each amino acid is 3 nitrogen bases long (ex- AAA, CGA, etc)
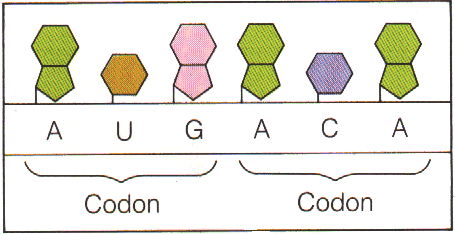
Codon: The genetic code (3 bases)
on m-RNA that codes for each amino acid.
Transcription (Seen in diagram above):
Process where the DNA code of one gene is changed into m-RNA code.
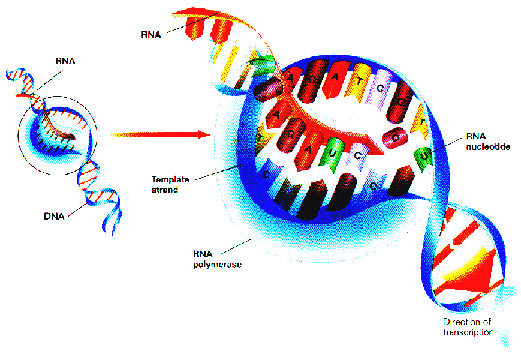
The area on this DNA that is an open loop is one gene new m-RNA
that is undergoing Transcription!
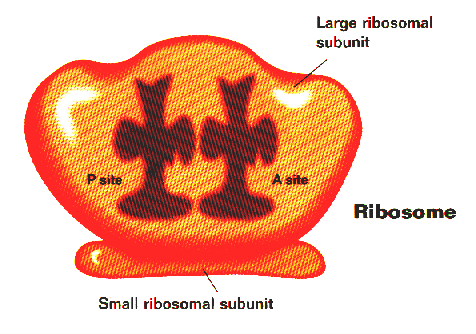
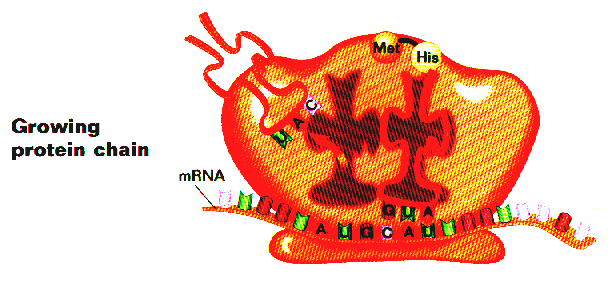
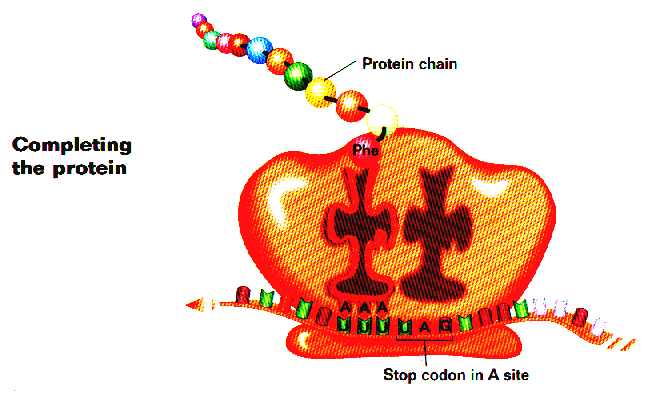
Translation: Process where the gene
code in m-RNA is read by a ribosome & translated into amino acid code, making
a protein.
For translation to work, the ribosome fits the triplet (3 letter)
code of m-RNA to the triplet of t-RNA. This lines the amino acids up in the
correct order.
 ---->
----> ---->
----> 
Sample Problem:
DNA Code: ---TTT -CCT
GAT ACT
m-RNA Code: ____ ____ ____ ____
t-RNA Code: -____ ____ ____ ____
Amino Acids: ____ ____ ____ ____
 ----------------------
---------------------- 
Slichter
A. messenger-RNA: (m-RNA) copies the DNA code of a gene to carry out of nucleus.


 ---->
----> ---->
----> 