Ch. 18
Genetic Engineering
Forces of change
1. Mutation: changed content of genetic message (Nucleotide
altered, added, or removed) ( Ex.--- T changed to C )
2. Recombination: Gene moved to different chromosome or location
on chromosome
Recombination: provides genetic variability
Changes in position
1. gene transfer: segment donated to new chromosome
Example: AIDS
2. reciprocal recombination: chromosomes trade segments
Example : cross-over
3. chromosome assortment: meiosis (sexual reproduction)
Gene transfer: movement to other chromosome
locations
Plasmids : small, circular genomes
found in bacteria
Restriction endonucleases : cut
DNA double strands (isolating certain genes)
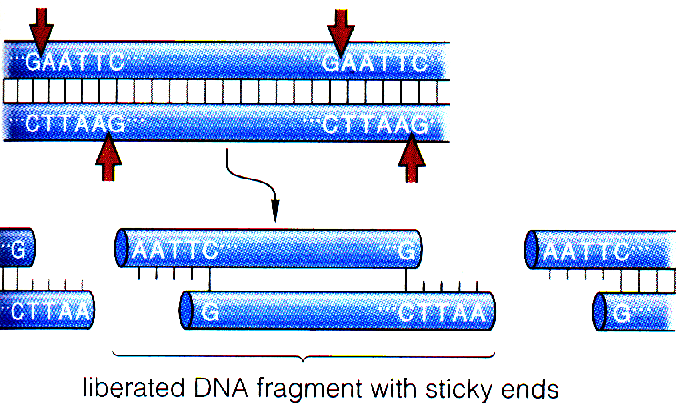
Restriction endonuclease cuts the nucleotide sequences shown
by both arrows. The single strands of DNA at both ends are referred to as
sticky ends.
DNA ligase : rebonds any two fragments
of DNA
Example : interferon (blood protein which increases human
resistance to viral infection)
*Restriction endonucleases
cut interferon gene from human DNA.
*DNA ligase bonds the fragment
into a bacterial plasmid.
*Bacterial cell (or yeast)
clones human interferon we then use.
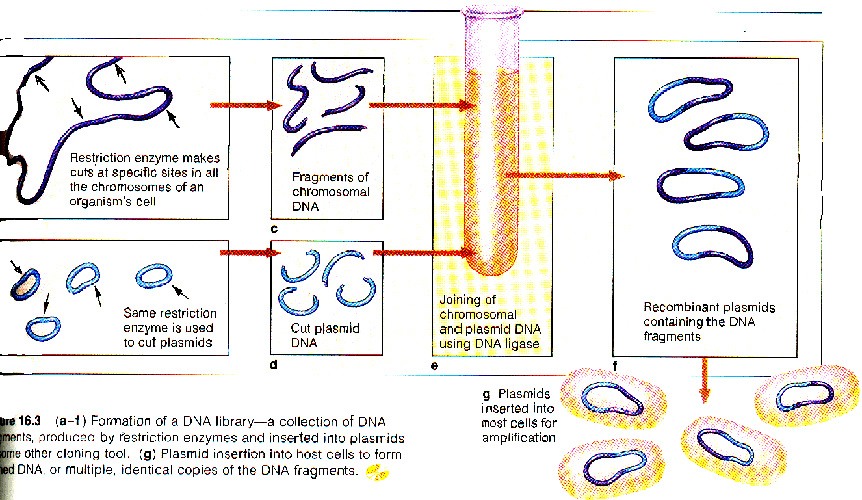
The diagram above shows the mechanics of cutting a gene
from one organism and placing it into a plasmid. The plasmid is then used
to insert the gene into the new host organism.
Examples of genetic engineering
1. disease, insect, or frost resistant veggies (corn, tomatoes,
strawberries)
2. larger salmon (they make more growth hormone )
3. longer lasting flowers (less ethylene)
4. increased milk production in cows
Long & Slichter

