Organic Molecules: Review for Quiz
1. Organic: Molecules containing carbon (and in living
things) except CO2 and carbonates. (1 pt)
2. a.
Atom: Equal number of protons and electrons (1
pt)
b. Ion: Unequal number of protons and electrons (1 pt)
3. a) Carbon Ð backbone of organic molecules (2)
b) Hydrogen Ð energy carriers, component of water,
component of organic molecules (2)
c) Oxygen Ð Cell respiration, component of water,
component of organic molecules (2)
d) Nitrogen Ð Component of proteins, component of
nucleic acids (2)
4. Water Properties: (any 4 of the following - 8 pts)
a)
Transparency (Light can reach aquatic plants for photosynthesis)
b)
Universal Solvent (Many substances can be dissolved in and transport via blood
or sap.)
c)
Cohesion (Water sticks together so small animals can walk on water)
d)
Adhesion (Water sticks to other materials, so is pulled up the veins in trees)
e) Heat Capacity (water bodies or animal bodies stay
same temperature)
f) High boiling point (water rarely boils on earth, so
life can exist here)
g) Ice Density (Ice floats and insulates life beneath
it.)
h) Evaporation (Evaporation cools off cells)
5. A) Proteins, B) Carbos,
C) Nucleic Acids, D) Lipids (4 pts)
6. (1 pt).
7.
(1 pt) 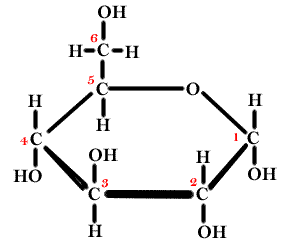
8. a) Dehydration (Condensation)- Bonds monomers to
form polymers, removing water as the bond is form. (1
pt)
b)
Hydrolysis - Bonds between
polymers broken to form monomers. Water is put back into each bond. (1 pt)
9. Importances of Proteins (Any 3 of the following - 6 pts)
a) Enzyme Catalysis - Amylase
b)
Body Defense - Antibodies
c)
Transport - Hemoglobin
d)
Body structure / Support - Collagen
e)
Motion - Actin
f) Regulation Ð Protein hormones like Insulin
10. C6H12O6 (1 pt)
11. Monosaccharides: glucose, fructose, galactose (2)
Disaccharides: sucrose, maltose, lactose (2)
Polysaccharides: starch (amylose), glycogen,
cellulose, chitin (2)
12. Named carbos and a function of each (any 4 Ð 8 pts)
a)
Glucose Ð Energy source for all cells
b)
Glycogen (animal starch) Ð long term energy storage for animals
c)
Amylose (plant starch) Ð long term energy storage for plant cells
d)
Cellulose Ð Structure of plant cell walls.
e)
Chitin Ð Structureal polysaccharide of insect or crustacean exoskeletons.
13. Named lipids and function of each (6 pts)
a)
Fats & Oils Ð Energy storage
b)
Chemical Messengers Ð Steroid hormones (cholesterol, estrogen, testosterone,
progesterone)
c)
Lipid bilayers of cell membranes (Phospholipids)
14. a) Saturated - fatty acids with mostly single bonds
between carbons (has lots of C-H bonds) (1 pt)
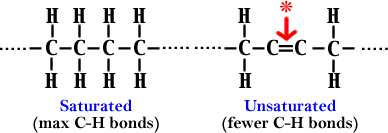
b) Unsaturated Ð fatty acids with some double bonds
between carbons (has less C-H bonds) (1 pt)
15. Monomers of triglycerides: (2 pts)
a)
fatty acids
b)
glycerol
16. Lipids are largely nonpolar because they are made
mostly of nonpolar C-H bonds (or have many C-H bonds). (1 pt)
17. Phospholipids contain a glycerol base with 2 fatty
acids and a phosphate group. (1 pt)
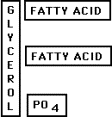
Period
1 (57 pts total)
Period
2 (50 pts total)
Period
4 (50 pts total)