
Replication: The duplication of DNA to make 2 identical copies of DNA prior to cell division.
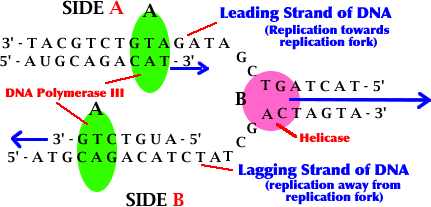
3' --------> 5' strand of DNA is read to replicate DNA.
Leading Strand of DNA - Strand of DNA synthesized continuously toward replication fork.
Lagging Strand of DNA - Strand of DNA formed in fragments (Okazaki fragments) on strand away from replication fork.
Helicase - Enzyme that untwists & opens DNA molecule (like a zipper).
RNA Primase - Enzyme that adds a short RNA primer to start replication (RNA primer later removed.).
DNA Polymerase III - Adds DNA nucleotides to new DNA strand in 5' ---> 3' direction.
DNA Polymerase I - Enzyme removes RNA primer & replaces it with DNA nucleotides.
DNA Ligase - Joins neighboring nucleotides or Okazaki fragments together.
Mistakes occuring during replication are removed by enzymes!
Semi-conservative Replication: This process creates 2 new strands of DNA, each having one strand from the original DNA, each having a newly synthesized strand.
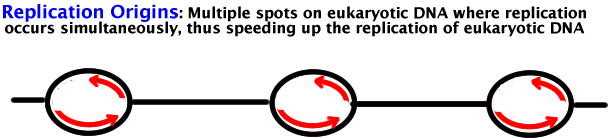
Replication Origins : Multiple sites on eukaryotic chromosomes that code for initiating replication. Eukaryotic chromosomes can thus replicate the same DNA at multiple sites much faster. Prokaryotic chromosomes replicate from one site (slower!).