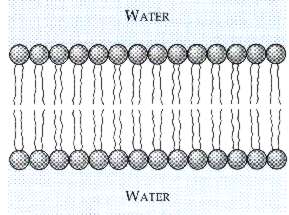
* a. Plasma membrane
* b. Central nucleus (usually). DNA is covered with histones (a type of protein).
* c. Membrane-bound organelles (like mitochondria, chloroplasts, vacuoles, ER, etc...) within cytoplasm
Examples of Eukaryotic Cells:
Examples of Eukaryotic Cells:
a) Animal Cells --------- b) Plant Cells -------- c) Fungal Cells -------- d) Protist Cells
Organelles: Any discrete structure within a cell which has a specific function. Organelles
a) are each surrounded by a plasma membrane.
b) separate and compartmentalize chemical reactions in time and space (They organize reactions so they can be more efficient.).
c) are only found in all eukaryotic cells (They do not exist in prokaryotes.).
Acellular: Contains no cells.

1) Plasma membrane: Outer surface of animal cells. Phospholipid bilayer. Controls entry & exit of molecules.
2) Nucleus: information center of cell.
3) Endoplasmic reticulum: Tubules for transport and synthesis of large organic molecules. Often continuous with nuclear envelop. Organizes cell interior.Largest organelle, readily visible. Nuclear envelope: double membrane layer, restricts passage of molecules. Chromosomes: contain heredity information (made of DNA & proteins).
Nucleolus: in center of nucleus- manufactures ribosomes.
a) Rough ER (rER): Manufacture proteins for export
Ribosomes: assist in protein synthesis.
b) Smooth ER (sER): Lack ribosomes so smooth surface. Synthesize carbohydrates and lipids. Associated with detoxification.
4) Lysosomes: vacuole containing digestive enzymes. Functions:
a. Enzymes catalyze breakdown of macromolecules
b. Alter internal pH
c. Digest worn-out cell components
d. Digest pathogens engulfed by WBC's
e. Participate in selective cell death
 5)
Mitochondria: Provides chemical energy (ATP) for
cell
5)
Mitochondria: Provides chemical energy (ATP) for
cell
6) Chloroplasts: photosynthesis (trap light energy in plants).Double membrane Possesses own DNA: produces own RNA (ribosomes) Capable of replication
Occur in plants and algae. Double membranes. Possess own DNA, produce own RNA (ribosomes).
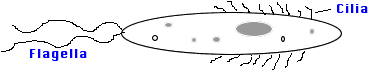 7)
Flagella and Cilia: motility
7)
Flagella and Cilia: motility
Flagella: long microtubule strands, locomotion
Cilia: short microbutule strands. Locomotion, pass fluids, react to sound waves
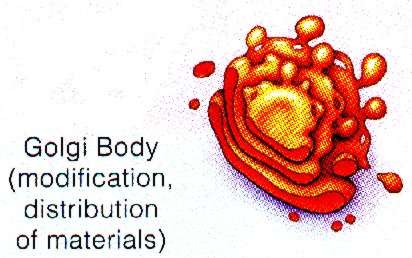
8) Golgi Apparatus:
9) VacuolesModification, packaging & distribution of finished macromolecules (carbos & lipids)
[Relationship of ER to nucleus, golgi apparatus, and cell membrane #1]
[Relationship of ER to nucleus, golgi apparatus, and cell membrane #2]
Membrane bound organelles for storage of macromolecules, water, or cellular wastes.
10) Cell Wall
Rigid outer layer of plant cells. Made of cellulose microfibrils.
|
Animal Cells
|
Plant Cells
|
| 1. No Chloroplasts | 1. Chloroplasts present (usually) |
| 2. No Cell Wall | 2. Cell Wall |
| 3. Usually no large central vacuole. | 3. Most have large central vacuole. |
| 4. Carbohydrates stored as glycogen. | 4. Carbohydrates stored as starch. |
| 5. Has lysosomes. | 5. Generally lacks lysosomes. |
| 6. Shape- Changeable, usually rounded. | 6. Shape- Rigid, often with 'straight' edges. |
[Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells] - Know for exam!
(Info on Today's Quiz)
Cells - Building blocks of all life.
Tissues - Group of similar cells. (nervous tissue, cardiac tissue, skeletal muscle tissue)
Organs - Several types of tissues grouped together to help do a certain function. (heart, brain, liver)
Organ Systems - Several different organs working together to perform the same job. (Ex: esophagus, stomach, small intestine etc are part of the digestive system)
Organism - Many different organ systems that work together to make one living thing.
Online Reviews of Cells - These links can help you familiarize yourself with the different cell organelles, what they look like and what they do!
1) Bring lab books next time. We will finish the microscope lab, then start the cell lab where you will definitely need the lab books!
2) Read in your text book:
Psychedelic Tasmanian Wolf Texts: pp 68-74, 77-83
Nemo Book: pp 70 - 78, 79-85
3) Review for Clicker Quiz on Prokaryotic Cells (See Online Review: First Review of Prokaryotic Cells as there are new pictures in this review that you will be required to know for this quiz!)