Cell Cycle
|
Reading: Old Books (Nemo) (5th Edition)
|
Reading: New Books (6th Edition)
|
| a. Read pp. 208-218 | a. Read 207-217 |
| b. Read pp 224-225 | b. Read 223-224. |
| c. See pg 224 for glossary of terms! | c. See pg 224 for glossary of terms! |

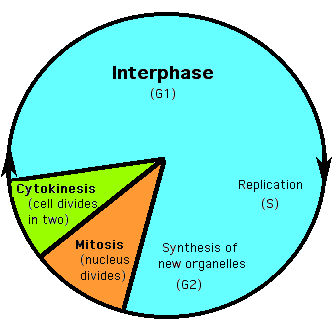
Cell Cycle: Cell Life Cycle. The repeating sequence of growth and division through which eukaryotic cells pass each generation.
Stages of Cell Growth
1. G1 phase: primary growth phase. Cell does its 'job'.
2. S phase: DNA replication
3. G2 phase: Chromosome condensation, cell organelle replication
4. M phase: mitosis (nuclear division) (Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, & telophase)
5. C phase: cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division), daughter cells form

[Interphase] - Longest stage of cell cycle (The part where it does not divide). (G1, S, G2). Human cells contain 46 chromosomes during the G1 stage of interphase. This is doubled to 92 during the S stage of interphase.
Mitosis - Nuclear Division
|
Animal Cells
|
Plant Cells
|
| Late in anaphase, the plasma membrane pulls inward forming a cleavage furrow, which divides the cell in two during telophase. | After anaphase, a new cell wall forms between the two new nuclei to create two cells. |
| A centriole is found at each pole during mitosis. | No centrioles are found in plant cells. |
Uses of Mitosis in Eukaryotic Cells:
a. during growth of the individual.
b. when tissues have been damaged and need to be repaired (as in healing of a cut).
c. to reproduce asexually.
Cancer: Disorder in which some of the body's cells lose the ability to control their growth.
Tumor - repeated, uncontrolled cell division to form a mass of cells. This can happen in any organ. Some tumours grow large and spread to other parts of the body (metastasis). The diseases caused by the growth of tumours is known as cancer.
Cell Cycle: An Interactive Animation (Cell's Alive!)
Mitosis: An Interactive Animation (Cell's Alive!)
Cell Biology and Cancer (National Cancer Institute)
NOVA Online - Cancer Warrior - How Cancer Grows Step through animation with text - No sound.
Summer 2003 The Biology of Cancer (Harvard) - Be sure to disable popup blocker to view animations.
How Tumor Suppressor Genes Block Cell Division (McGraw Hill)
Mitosis & Cytokinesis (McGraw Hill)
Cell Division Bioclip (with music) (University of Wisconsin)
Mitosis & Cell Plate Formation in Blood Lily Cells (Mitosis World) (Videoclip)
Plant and Animal Cell Division Movies
Mitosis Animation (About Biology)
Mitosis Animations (Alternative Formats -Quicktime & Shockwave)
Stem Cells (Gene Almanac)
Cloning:
Cloning 101: Animation - Stem Cells (Gene Almanac)
Gene Cloning (Interactive Concepts in Biochemistry)
The Cloning Process (CNN)
Clonezone: Therapeutic or Reproductive (Canadian Museum of Nature)
Click and Clone (Utah.edu) - Clone a Mouse Online
Cloning Myths (Genetic Science Learning Center)