Cells need energy--> growth, reproduction, for chemical reactions,
movement, etc..
Bonds between C-H in organic molecules store energy for long
periods. Energy is needed in small doses, or cell is overwhelmed. Small amounts
of energy are stored in the bonds of ATP.
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate. Short-term
energy storage molecule of all cells.
Cells break C-H bonds & store the released energy as ATP for
energy use when needed. Cells mainly use ATP energy.
AMP + Energy ---> ADP ADP + Energy --->
ATP
Photosynthesis
Plant cells convert light energy into chemical (C-H) energy in
sugars.
6CO2 + 6H2O ------------> C6H12O6 +
6O2
Sunlight is a mixture of different colored light. Each color
is a different wavelength, and thus a different level of energy to be used.
Photosynthetic Plant Pigments: Chemicals
that absorb light, & have their electrons then get energized. The energized
electrons get passed on to make ATP or other energy carriers.
Examples of Plant Pigments:
Chlorophyll a & b- absorbs blue & red light, reflects (doesn't
use) green.
Xanthophyll- reflects yellow
Carotene- reflects orange
2 parts to Chloroplast:
a. Grana- contains chlorophyll. looks like coin stacks. Where light dependent
reactions occur.
b. Stroma- No chlorophyll. Where sugar is made. Site of "dark" reactions.
A simplified diagram of a chloroplast is shown above.
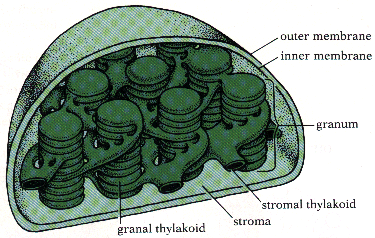
A more detailed diagram of a chloroplast is shown above.
2 Major Steps (reactions) of Photosynthesis:
1. Light Dependent Reactions- Makes ATP, NADPH2, O2. Needs light to occur.
2. Light Independent Reactions- Makes sugars. May occur in light or dark.
Light Dependent Reactions- Actually many reactions. Occurs only in light.
Light energy is converted to chemical energy of ATP & NADPH. NADPH is a H+ &
energy carrier. The ATP & NADPH accumulate & are moved to the stroma where they
are used to make sugar.
ATP is a short-term energy carrier.
NADPH is a short-term energy carrier &
also carries H+ ions from the breakdown of water.
Two Main Parts of the Light Dependent Reactions:
A. Cyclic Photophosphorylation: Excited electrons are cycled through a series
of electron acceptors to make ATP.
B. Noncyclic Photophosphorylation:
a. Light energizes chlorophyll, which splits H2O (photolysis). The O2 is
released to air. The H+ are used to make NADPH2 .
b. More light energizes another chlorophyll which releases energy to make
2 ATP.
c. A different wavelength of light energizes another chlorophyll, which
then releases energy to make 2 NADPH2.
Long & Slichter


