PCR
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR):
PCR is a technique for creating large quantities of replicate copies of
DNA, starting with a small amount of starting DNA. Literally in a few hours,
the amount of DNA can be increased billions of times.
Use: If a small amount of blood, skin, or other
DNA containing sample is found at a crime scene, PCR can be used to create
a larger sample of the DNA for use in DNA fingerprinting.
Method of PCR:
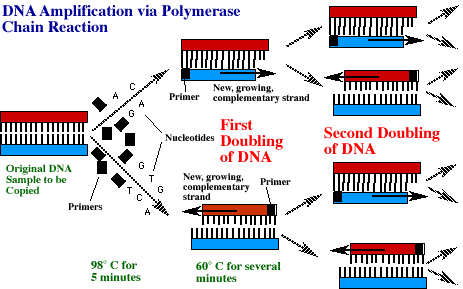
1. Place in PCR machine.
2. Heat sample , 5 minutes at 98¾C. This separates the double stranded
original DNA, creating 2 single strands of DNA.
3. Add RNA primers (short RNA strands that provide a starting sequence).
4. Add nucleotides source (A, T, C, G).
5. Add DNA polymerase enzyme (Adds nucleotides to strand, finishing synthesis
of DNA replicates.)
6. Cool to 60¾C, incubating for several minutes.
7. RNA primers attach to single strand DNA, nucleotides now added.
8. Two complete DNA copies are now made.
9. Repeat many more times to create more copies.
Slichter

