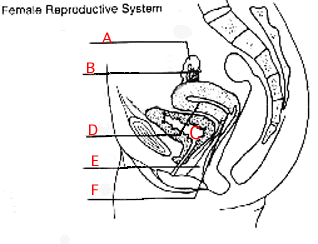
 A) Ovary
- In animals it is the organ in which eggs are produced by meiosis.
A) Ovary
- In animals it is the organ in which eggs are produced by meiosis.Structure & Function
 A) Ovary
- In animals it is the organ in which eggs are produced by meiosis.
A) Ovary
- In animals it is the organ in which eggs are produced by meiosis.
B) Oviduct - In vertebrates it is the passageway through which ova (eggs) travel from the ovary to the uterus. Frequently, it is the site of fertilization of the ova by a sperm.
C) Bladder - The urinary bladder, where urine is stored until release through the urethra. It is found anterior to (forward of) the uterus and vagina. A developing fetus will expand the uterus and eventually will exert pressure on the bladder.
D) Uterus - In mammals, a chamber in which the developing embryo is contained and nurtured during pregnancy.
E) Vagina - In mammals, a thin-walled chamber that forms the birth canal through which the baby is born. It is also the site where sperm are deposited during copulation.
F) Cervix - In mammals, the neck of the uterus, which opens to the vagina.
Vulva -
Urethra - The tube carrying urine from the bladder to the exterior of mammals.
Large Intestine - It is the portion of the digestive system immediately after the small intestine. It is the site of water and mineral absorption and collects the indigestible waste. The vagina and to some extent the uterus are found between the bladder and the large intestine. As in the bladder, a developing fetus will expand the uterus which will eventually exert some pressure on the large intestine.
